WHAT SHOULD ONE KNOW ABOUT RHEUMATOID ARTHRITIS?
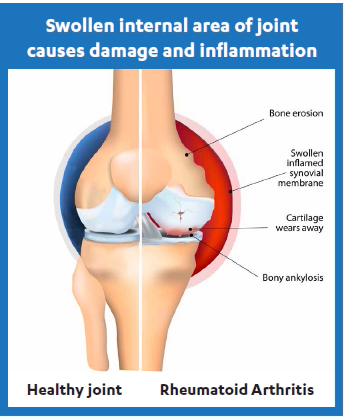
Rheumatoid Arthritis (RA) is a life-long disease and mostly affects the joints in the wrist, hands, feet, spine, and knees. Affected joints tend to become red, swollen and ultimately result in the following:

Pain

Stiffness

Loss of function
(difficulty moving, lack of balance and joint deformity)
Why does this disease occur?
The immune system is like an army of soldiers - it is the first and last line of defence, protecting the body against harmful germs.
But when the body's immune system mistakenly attacks its own healthy cells, it results in the development of certain conditions classified as autoimmune disorders.
In RA, the immune system attacks the internal joint linings.
Who is at a higher risk of getting rheumatoid arthritis?
Certain risk factors make a person more likely to have RA. These include:

Age
RA can occur at any age, but is more common in adults above 60 years.

Gender
RA affects women two-to-three times more as compared to men.

Heredity
People having specific genes have a higher chance of developing RA, further increasing the likelihood when exposed to other risks.

Smoking
Cigarette smoking increases the risk of developing RA and worsens the existing RA.

Women with no children
Women who have never given birth may be at a greater risk of developing RA.

Early-life exposure
Children of smoking mothers are at double the risk of developing RA as adults.

Obesity
Higher body weight increases the risk of RA.
SPOT THE SYMPTOMS
What are the typical symptoms?

Pain or ache in multiple joints

Tenderness and swelling in multiple joints
Stiffness in multiple joints

The same symptoms on both sides of the body (both hands or both knees can be affected)
Are there any early warning signs?
Before the appearance of main symptoms, a person may have some early warning signs like:

Fatigue
May affect everyday activities, relationships, sex life and productivity at work

Slight fever
A slight fever may occur before any noticeable effects on the joints

Weight loss
A person may lose his/her appetite, which can result in weight loss
Joint stiffness
Affects a person particularly in the morning or after periods of inactivity

Numbness and tingling
Can occur in hands and feet and can result in loss of sensation
Let’s understand few terms associated with rheumatoid arthritis
RA flare-ups: Symptoms of RA can become worse for brief periods called flare-ups.
Remission: The times when symptoms get better.
RA flare-ups can be hard to predict, but it is possible to reduce the frequency of flare-ups and minimize or prevent long-term damage to the joints with appropriate treatment.
What if rheumatoid arthritis is not treated in time?
Untreated RA might have alarming consequences. These may include:
- Damaged and deformed joints
- Loss of function and disability
- Coronary artery disease (narrowing or blocked blood vessels of the heart)
- Anaemia, which is a deficiency of red blood cells and oxygen in the blood
- Early death
- Depression and nervous system disorders
Remember, these complications can be avoided when one visits a doctor at the earliest.
HOW IS RHEUMATOID ARTHRITIS MANAGED?
When to visit a doctor?
Visit a doctor immediately if any of the symptoms of RA are noticed. An early visit to the doctor can help determine the exact cause and enable quicker diagnosis. Early diagnosis of RA is crucial as it can prevent further joint damage and thus, prevent the condition from getting worse.
What should one know regarding the diagnosis of rheumatoid arthritis?
Diagnosis of RA is challenging. To arrive at the diagnosis, a doctor may ask several questions pertaining to medical history, symptoms, etc. and may prescribe some blood tests and joint scans.

Physical examination
The doctor will check the joints of a person for swelling, tenderness, and range of motion

Blood Tests
The doctor will check for certain factors which are responsible for RA

Joint scans
The doctor will conduct a detailed examination of the joint structure
If the family doctor feels a person has RA, he/she will refer the patient to a specialist handling joint diseases, called a Rheumatologist.
GOALS OF RHEUMATOID ARTHRITIS TREATMENT
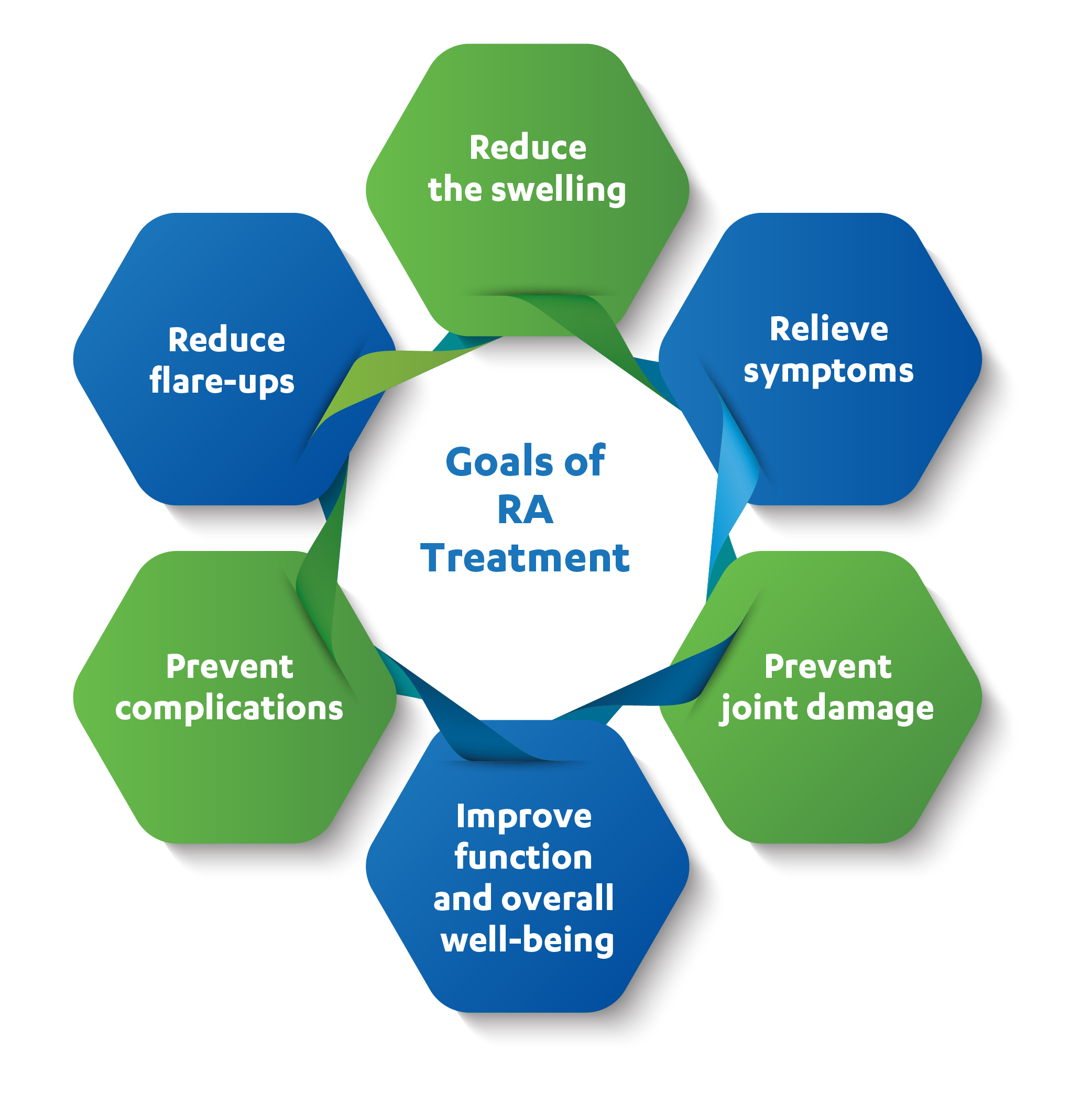
What does the treatment include?
Below are few treatment approaches for treating RA. The doctor will choose the best treatment approach depending on the severity of the symptoms.

Initial lifestyle Changes
Right eating, exercise, and good sleeping habits may be beneficial.
Medications
The prescribed medicines help relieve pain, prevent or slow down joint damage, lower the disability and enable a person to live well.
Surgery
Based on the disease severity, a doctor may recommend surgery to reduce pain and fix deformities.




